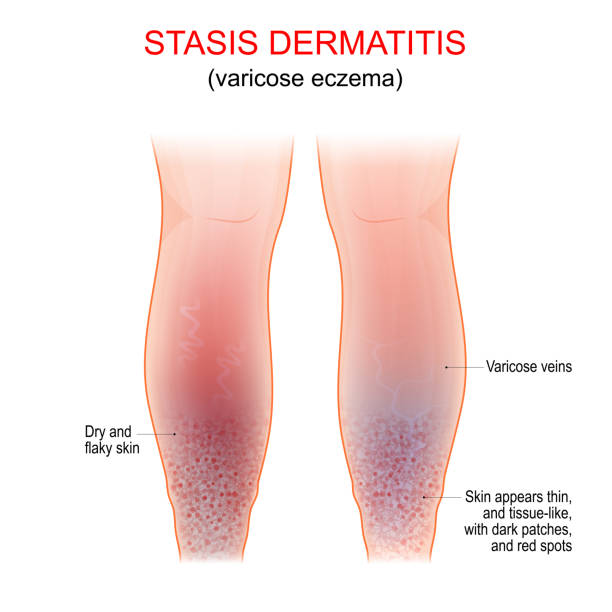
Stasis dermatitis, a chronic inflammatory skin condition, primarily affects the lower legs due to compromised blood circulation.
Often seen in older adults, this condition is closely linked to venous insufficiency—a disorder in which the veins struggle to send blood from the legs back to the heart. If left untreated, stasis dermatitis can lead to more severe complications, including ulcers and infections.
Understanding its causes, recognizing symptoms early, and exploring both conventional and advanced treatment options are crucial steps in effectively managing and mitigating the impact of stasis dermatitis.
Causes of Stasis Dermatitis
The underlying cause of stasis dermatitis is chronic venous insufficiency (CVI).
In CVI, the veins in the legs fail to properly circulate blood back to the heart, causing blood to pool in the lower extremities. This pooling increases venous pressure, eventually leading to fluid leakage from the veins into surrounding tissues. Over time, the stagnant blood and fluid provoke an inflammatory response in the skin, resulting in the symptoms associated with stasis dermatitis.
Several factors contribute to the development of CVI and, consequently, stasis dermatitis:
- Aging: As we age, the valves in our veins may weaken, making it more difficult for blood to return to the heart. This natural wear and tear increases the risk of venous insufficiency and related skin conditions.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts additional pressure on the veins in the legs, exacerbating the strain on venous circulation and increasing the likelihood of CVI.
- Prolonged Standing or Sitting: Occupations or lifestyles that involve extended periods of standing or sitting can impair blood flow in the legs, contributing to venous insufficiency.
- History of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): Individuals with a history of DVT—a condition where blood clots form in deep veins—are at a higher risk for venous insufficiency and stasis dermatitis.
- Pregnancy: The increased blood volume and pressure on the pelvic veins during pregnancy can sometimes lead to venous insufficiency, which may persist and evolve into stasis dermatitis in later years.
Symptoms of Stasis Dermatitis
Stasis dermatitis is characterized by a range of symptoms, varying in intensity depending on the severity of venous insufficiency. These symptoms often progress through several stages:
- Early Symptoms: In the initial stages, stasis dermatitis manifests as redness, itching, and mild swelling, particularly around the ankles. The skin may appear shiny and taut, with occasional scaling or flaking.
- Intermediate Symptoms: As the condition progresses, the affected skin may thicken and develop a brownish discoloration due to the deposition of hemosiderin—a byproduct of red blood cell breakdown. This stage is often accompanied by increased itching and discomfort.
- Advanced Symptoms: In severe cases, the skin becomes increasingly fragile and prone to cracking. Ulcers, often referred to as venous stasis ulcers, may develop, typically around the inner ankles. These ulcers can be painful and slow to heal, posing a risk for secondary bacterial infections.
- Complications: If not properly managed, stasis dermatitis can lead to chronic venous ulcers, cellulitis, and in rare cases, lipodermatosclerosis—a condition where the skin and underlying fat tissue become hardened and scarred.
Diagnosis and Evaluation of Stasis Dermatitis
A timely and accurate diagnosis of stasis dermatitis is essential for effective management. Healthcare providers typically base their diagnosis on a combination of clinical examination, patient history, and assessment of risk factors.
- Clinical Examination: During the physical exam, the doctor will assess the skin for signs of inflammation, discoloration, and ulcers. They will also evaluate the extent of swelling and any associated symptoms like itching or pain.
- Patient History: Understanding the patient’s medical history, including any previous episodes of DVT, varicose veins, or other vascular conditions, is crucial in diagnosing stasis dermatitis. The doctor may also inquire about lifestyle factors such as occupation, physical activity levels, and any family history of venous disorders.
- Diagnostic Tests: In some cases, additional diagnostic tests may be necessary. A Doppler ultrasound is commonly used to assess blood flow in the veins and identify any underlying venous insufficiency. This non-invasive test helps rule out other potential causes of the symptoms, such as lymphedema or peripheral arterial disease.
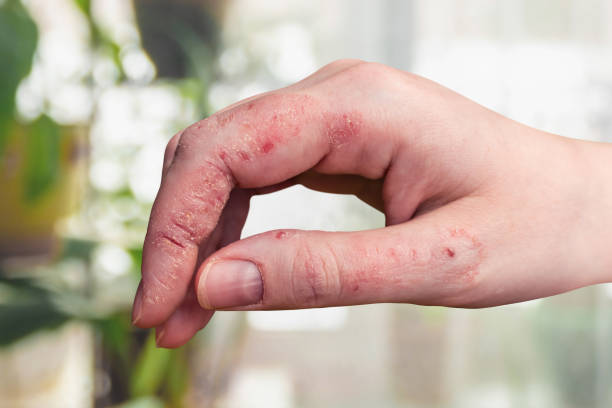

Treatment Strategies for Stasis Dermatitis
Effective treatment of stasis dermatitis requires a multi-pronged approach that addresses the symptoms and the underlying causes of venous insufficiency. The goal is to reduce inflammation, improve blood circulation, and prevent complications.
- Compression Therapy: Compression stockings or bandages are a cornerstone of stasis dermatitis treatment. By applying graduated pressure to the legs, these garments help reduce swelling, enhance venous return, and prevent the pooling of blood. Patients are often advised to wear compression stockings daily, especially during periods of prolonged standing or sitting.
- Topical Medications: Corticosteroids are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and alleviate itching. These topical medications can be applied directly to the affected skin to provide relief from discomfort. In addition, emollients or moisturizers are used to hydrate the skin and prevent cracking. For patients with dry, scaly skin, a combination of corticosteroids and moisturizing agents may be recommended.
- Wound Care: When ulcers are present, proper wound care is critical to promote healing and prevent infection. This involves cleaning the ulcer, applying appropriate dressings, and, if necessary, using topical or systemic antibiotics to treat any bacterial infections. Advanced wound care products, such as hydrocolloid or foam dressings, may be used to maintain a moist healing environment and protect the ulcer from further damage.
- Surgical Interventions: For patients with severe venous insufficiency who do not respond to conservative treatments, surgical options may be considered. Procedures such as vein ablation, sclerotherapy, or vein stripping aim to remove or close off the malfunctioning veins, thereby improving blood circulation and reducing the symptoms of stasis dermatitis. Endovenous laser therapy (EVLT) and radiofrequency ablation are minimally invasive techniques that have shown promising results in treating severe cases.
- Lifestyle Modifications: In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle changes play a vital role in managing stasis dermatitis. Patients are encouraged to engage in regular physical activity, such as walking or swimming, to promote healthy circulation. Elevating the legs when sitting or lying down can help reduce swelling while maintaining a healthy weight alleviates pressure on the veins. Avoiding prolonged periods of standing or sitting is also essential to prevent exacerbation of symptoms.
Effective Preventive Measures for Stasis Dermatitis
Prevention of stasis dermatitis involves managing risk factors and adopting habits that promote healthy venous circulation. Key preventive measures include:
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in activities that stimulate leg muscles, such as walking, cycling, or swimming, can significantly improve venous return and reduce the risk of developing venous insufficiency. Regular exercise also helps maintain a healthy weight, further reducing strain on the veins.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy body weight is crucial in preventing stasis dermatitis. Excess body weight increases the pressure on the veins in the legs, exacerbating the risk of venous insufficiency. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, combined with regular physical activity, can help achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
- Leg Care: Proper leg care is essential in preventing the onset or worsening of stasis dermatitis. Elevating the legs periodically, especially after long periods of standing or sitting, can help reduce swelling. Wearing compression stockings as advised by a healthcare provider can also prevent blood from pooling in the lower extremities.
- Skin Care: Maintaining healthy skin is critical to stasis dermatitis prevention. Regularly moisturizing the skin helps prevent dryness and cracking, which can lead to infections. Using gentle, fragrance-free skin care products can minimize irritation and protect the skin barrier.
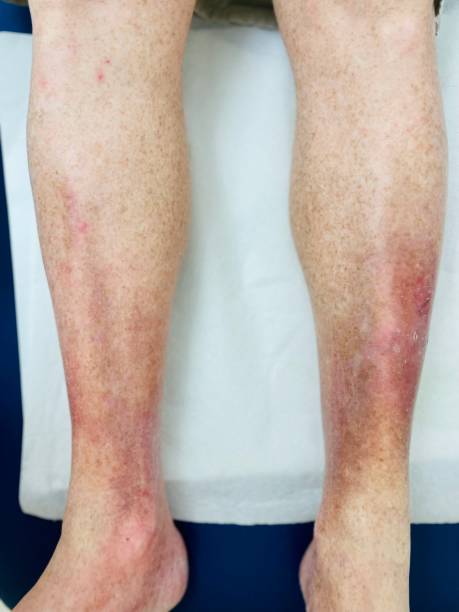
Recent Advances in Treatment for Stasis Dermatitis
In recent years, advancements in the treatment of stasis dermatitis have focused on improving the effectiveness of existing therapies and developing new, innovative approaches. Some of these advances include:
- Endovenous Laser Therapy (EVLT): EVLT is a minimally invasive procedure that uses laser energy to close off malfunctioning veins. This technique has gained popularity as it offers a less invasive alternative to traditional vein stripping, with shorter recovery times and improved outcomes for patients with severe venous insufficiency.
- Radiofrequency Ablation: Similar to EVLT, radiofrequency ablation uses heat generated by radiofrequency energy to close off problematic veins. This procedure is highly effective in improving blood circulation and reducing the symptoms of stasis dermatitis.
- Novel Topical Formulations: Researchers are exploring new topical treatments that combine anti-inflammatory agents with advanced moisturizing compounds. These formulations aim to provide more effective relief from the symptoms of stasis dermatitis while promoting skin barrier repair.
- Bioengineered Skin Substitutes: For patients with chronic venous ulcers, bioengineered skin substitutes are emerging as a promising treatment option. These products, made from living cells or synthetic materials, can be applied to the ulcer to promote healing and tissue regeneration.
Key Take Away
Stasis dermatitis can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life. The chronic nature of the condition, coupled with the discomfort and potential for complications, can lead to physical and emotional distress. Patients may experience pain, itching, and discomfort, which can interfere with daily activities and sleep. Visible changes in skin appearance might include discoloration and ulceration
Now that you understand the underlying causes of stasis dermatitis, implementing effective treatment strategies can help you manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life. For optimal results stay informed about the latest advancements in treatment options to ensure that you receive the most up-to-date and effective care. With proper management, the progression of stasis dermatitis can be significantly slowed, and complications can be minimized.
Subscribe to Kloud Iron’s 28-day fitness program and begin your journey toward optimal mental health and physical fitness. To learn more about Kloud Iron Fitness Hub’s offers, contact us today or message/follow us on Facebook and Instagram. We are also available on YouTube.


Leave Your Comment